As the core material basis of TCM clinical treatment, the quality and safety of Chinese herbal medicines are directly related to the medical effect and the health of the users. In the natural environment, if Chinese herbal medicines are not properly stored after harvest, especially under high temperature and high humidity conditions, it is easy to breed molds, among which poison-producing molds such as Aspergillus flavus are one of the main pollution sources. Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), as the most toxic and carcinogenic member of the aflatoxin family, has strong stability and concealment. Once contaminated Chinese herbal medicines, they may remain and enter the human body even after routine cleaning and processing. Long-term intake of Chinese herbal medicines contaminated by AFB1 may cause acute poisoning reactions, and increase the risk of chronic diseases such as liver cancer, posing a serious threat to public health. Therefore, rapid and accurate detection of AFB1 contamination in Chinese herbal medicines is a key link to ensure the quality and safety of Chinese herbal medicines.
Traditional methods for detecting AFB1, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS), etc., can achieve accurate quantification, but they require professional equipment, complex pretreatment processes, long detection cycles (usually hours to days), and rely on professional technicians to operate. In the daily quality monitoring of Chinese herbal medicine processing enterprises, rapid screening in the circulation link, and on-site sampling by regulatory authorities, traditional methods are often difficult to meet the needs of "fast results, low cost, and easy popularization". Especially in the season with high risk of mildew in traditional Chinese medicinal materials (such as the rainy season), a detection method that is easy to operate, short in detection time, and quick on-site judgment is urgently needed to achieve timely early warning and effective control of high-risk traditional Chinese medicinal materials.
Rapid identification methods and technical advantages of aflatoxin B1
At present, the rapid detection methods for AFB1 in traditional Chinese medicinal materials are mainly immunoassay techniques, such as colloidal gold immunochromatography, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), etc. Among them, colloidal gold immunochromatography test strips are widely used in grassroots detection and on-site screening by virtue of their "fast, simple and visual" characteristics. The core principle of this method is the use of antigen-antibody specific binding reaction: AFB1 antibody is pre-coated on the test strip. When AFB1 in the sample binds to the gold standard antibody, the formed complex will migrate to the T-line under chromatography. If the concentration of AFB1 in the sample reaches the detection threshold, the T-line will develop color; at the same time, the C-line is used as the quality control line, whether there is AFB1 or not, it will develop color to ensure the effective detection process.
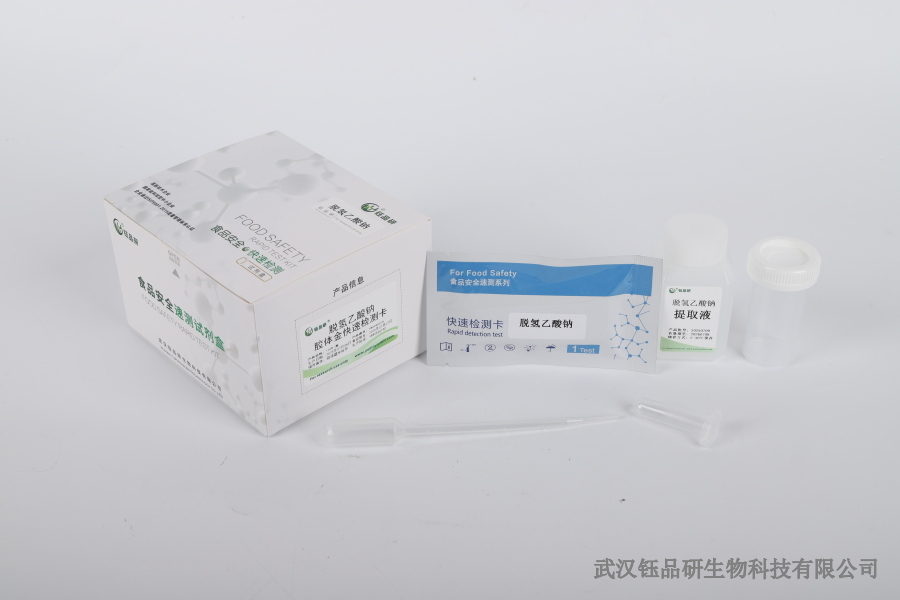
Wuhan Yupinyan Bio's rapid detection reagent solution
Wuhan Yupinyan Bio, as a technology enterprise focusing on the rapid detection of food safety, has been deeply involved in this field for many years. For the detection of AFB1 in the risk of mildew pollution of Chinese herbal medicines, it has developed a series of rapid detection reagent products. These reagents are based on mature immunochromatography technology and are designed in strict accordance with food safety testing standards. They can be tested within 15-30 minutes without the need for complex equipment. Operators can get started with simple training. During testing, simply take an appropriate amount of Chinese herbal medicine samples, perform simple pretreatment with matching extracts, and drop the treated liquid into the test card. By observing the color development of T-rays and C-rays (if the T-rays are clear, it is positive, and if the T-rays are not colored, it is negative), you can quickly determine the degree of AFB1 contamination in the sample. Compared with traditional detection methods, Wuhan Yupinyan Bio's AFB1 rapid detection reagent has the advantages of "high sensitivity (detection limit can reach μg/kg level), strong specificity, convenient operation, and controllable cost". It can be widely used in different scenarios such as Chinese herbal medicine planting bases, processing enterprises, and drug inspection institutions, providing efficient technical support for the quality and safety management of Chinese herbal medicines.
The problem of mildew pollution and AFB1 exceeding the standard of Chinese herbal medicine is one of the outstanding problems restricting the healthy development of the Chinese medicine industry. Through the introduction of rapid identification methods, especially the AFB1 rapid detection reagent of Wuhan Yupinyan Bio, "early detection, early warning and early disposal" of aflatoxin pollution in Chinese herbal medicines can be realized, ensuring the quality and safety of Chinese herbal medicines from the source, and building a strong defense line for the standardization and standardization of the Chinese medicine industry. In the future, with the continuous upgrading of technology, rapid detection technology will play a greater role in more Chinese herbal medicine varieties and complex matrix samples, helping the Chinese medicine industry to achieve high-quality development in the new era.